What Is SAS?
SAS is a set of solutions for enterprise wide business users and provides a powerful fourth generation programming language for performing tasks such as these:
- data entry, retrieval, and management
- report writing and graphics
- statistical and mathematical analysis
- business planning, forecasting, and decision support
- operations research and project management
- quality improvement
- applications development
Components of Base SAS Software
- Overview of Base SAS Software
- Data Management Facility
- Programming Language
- Elements of the SAS Language
- Rules for SAS Statements
- Rules for Most SAS Names
- Special Rules for Variable Names
- Data Analysis and Reporting
- Utilities
Overview of Base SAS Software
Base SAS software contains the following:
- a data management facility
- a programming language
- data analysis and reporting utilities
Data Management Facility
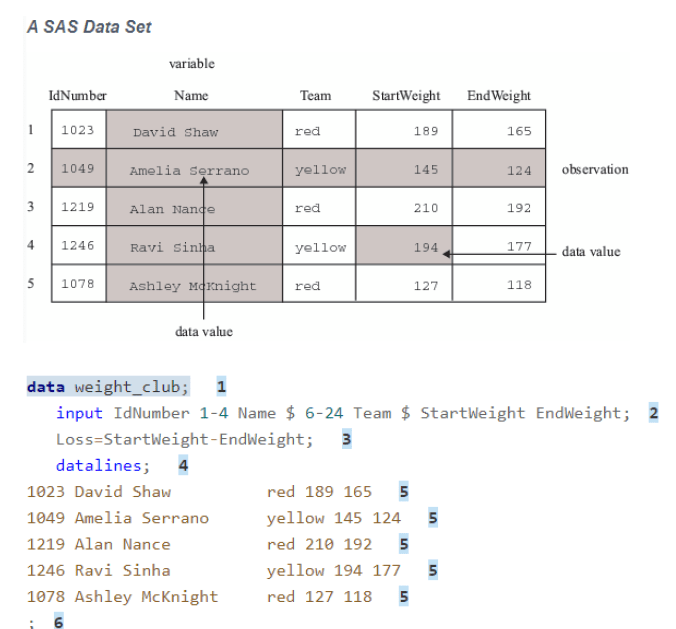
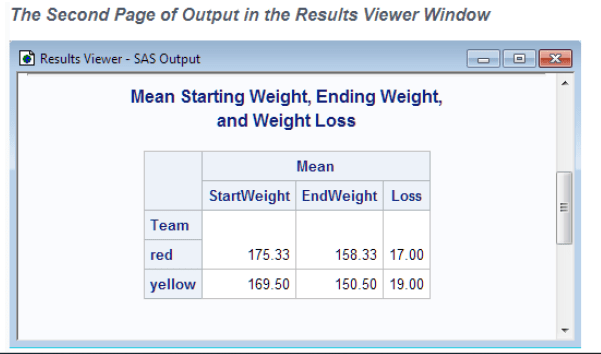
SAS organizes data into a table that is called a SAS data set. The following figure shows a
SAS data set. The data describes participants in a 16 week weight program at a health and
fitness club. The data for each participant includes an identification number, name, team
name, and weight (in U.S. pounds) at the beginning and end of the program.
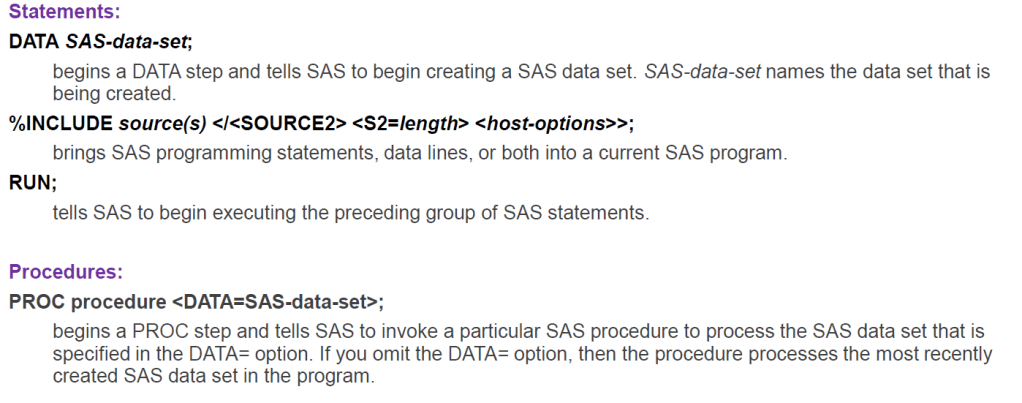
Rules for SAS Statements
- SAS statements end with a semicolon.
- You can enter SAS statements in lowercase, uppercase, or a mixture of the two.
- You can begin SAS statements in any column of a line and write several statements on the same line.
- You can begin a statement on one line and continue it on another line, but you cannot split a word between two lines.
- Words in SAS statements are separated by blanks or by special characters (such as the equal sign and the minus sign in the calculation of the Loss variable in the WEIGHT_CLUB example).
Rules for Most SAS Names
- A SAS name can contain from one to 32 characters.
- The first character must be a letter or an underscore (_).
- Subsequent characters must be letters, numbers, or underscores.
- Blank spaces cannot appear in SAS names.
Data Analysis and Reporting Utilities
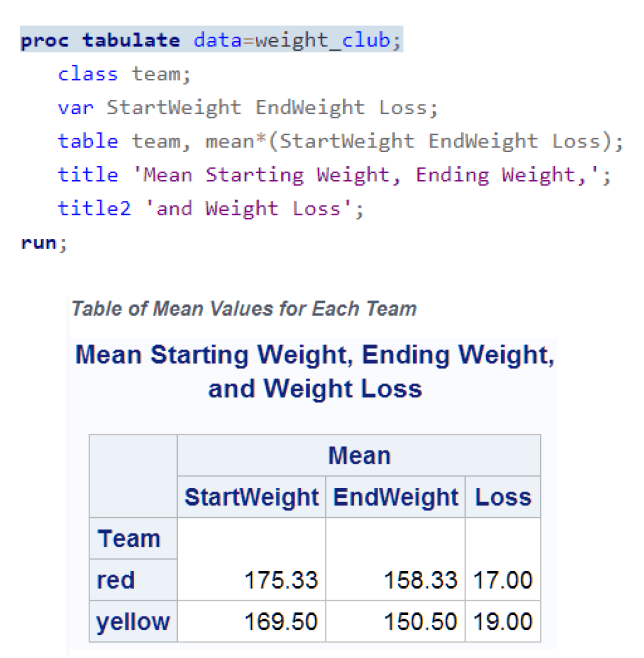
The SAS programming language is both powerful and flexible. You can program any number of analyses and reports with it.

Output Produced by the SAS System
A SAS program can produce some or all the following types of output:
- SAS data set
- SAS log
- report or simple listing
- other SAS files such as catalog
- external files or entries in other
- databases

Ways to Run SAS Programs
- SAS Windowing Environment
- SAS/ASSIST Software
- Noninteractive Mode
- Batch Mode
- Interactive Line Mode
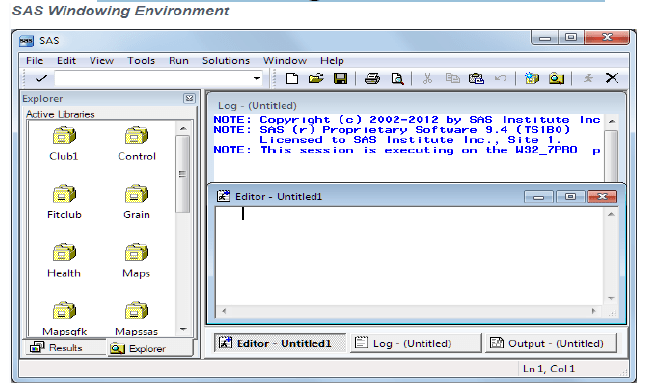
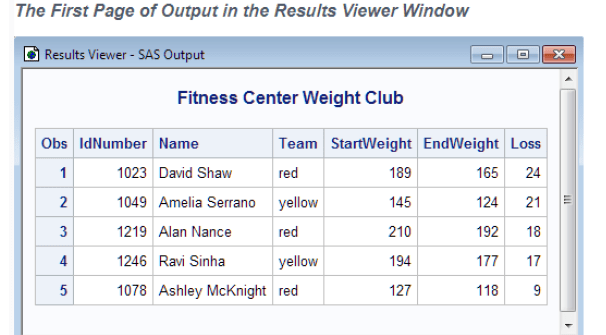
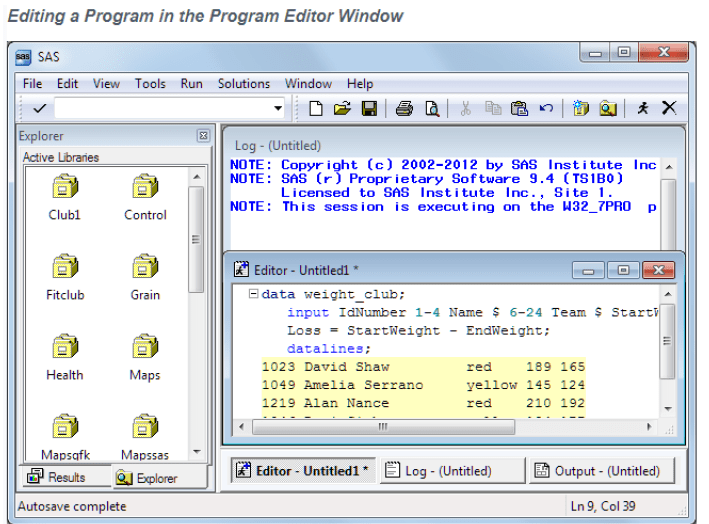
Running Programs in the SAS Windowing Environment
Summary

Leave a comment