System and architecture overview
An Amazon Redshift data warehouse is an enterprise-class relational database query and management system. •Amazon Redshift supports client connections with many types of applications, including business intelligence (BI), reporting, data, and analytics tools. •When you execute analytic queries, you are retrieving, comparing, and evaluating large amounts of data in multiple-stage operations to produce a final result. •Amazon Redshift achieves efficient storage and optimum query performance through a combination of massively parallel processing, columnar data storage, and very efficient, targeted data compression encoding schemes.
Data warehouse system architecture
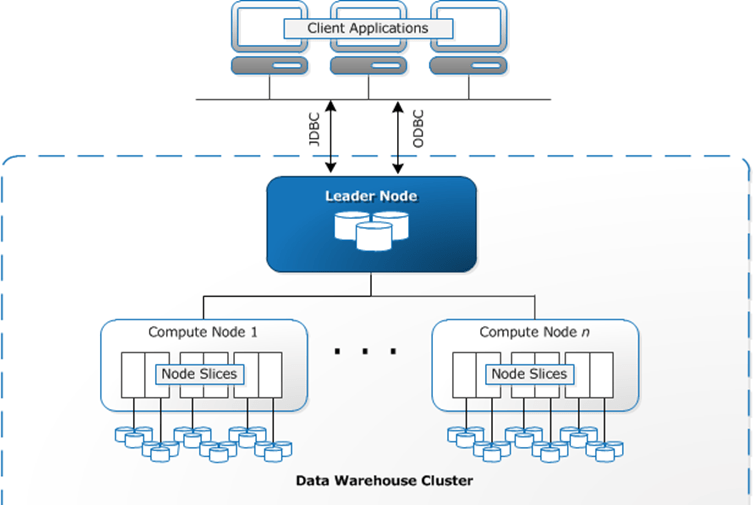
Data warehouse system architecture
Client applications: Amazon Redshift integrates with various data loading and ETL (extract, transform, and load) tools and business intelligence (BI) reporting, data mining, and analytics tools. Amazon Redshift is based on industry-standard PostgreSQL, so most existing SQL client applications will work with only minimal changes.
Connections: Amazon Redshift communicates with client applications by using industry-standard JDBC and ODBC drivers for PostgreSQL.
Clusters: The core infrastructure component of an Amazon Redshift data warehouse is a cluster. A cluster is composed of one or more compute nodes. If a cluster is provisioned with two or more compute nodes, an additional leader node coordinates the compute nodes and handles external communication. Your client application interacts directly only with the leader node. The compute nodes are transparent to external applications.
Leader node: The leader node manages communications with client programs and all communication with compute nodes. It parses and develops execution plans to carry out database operations, in particular, the series of steps necessary to obtain results for complex queries. Based on the execution plan, the leader node compiles code, distributes the compiled code to the compute nodes, and assigns a portion of the data to each compute node.
Compute nodes: The leader node compiles code for individual elements of the execution plan and assigns the code to individual compute nodes. The compute nodes execute the compiled code and send intermediate results back to the leader node for final aggregation.
Node slices: A compute node is partitioned into slices. Each slice is allocated a portion of the node’s memory and disk space, where it processes a portion of the workload assigned to the node. The leader node manages distributing data to the slices and apportions the workload for any queries or other database operations to the slices. The slices then work in parallel to complete the operation. •The number of slices per node is determined by the node size of the cluster. When you create a table, you can optionally specify one column as the distribution key. When the table is loaded with data, the rows are distributed to the node slices according to the distribution key that is defined for a table. Choosing a good distribution key enables
Internal network: Amazon Redshift takes advantage of high-bandwidth connections, close proximity, and custom communication protocols to provide private, very high-speed network communication between the leader node and compute nodes. The compute nodes run on a separate, isolated network that client applications never access directly.
Databases: A cluster contains one or more databases. User data is stored on the compute nodes. Your SQL client communicates with the leader node, which in turn coordinates query execution with the compute nodes
Performance
Amazon Redshift achieves extremely fast query execution by employing these performance features.
- Massively parallel processing
- Columnar data storage
- Data compression
- Query optimizer
- Result caching
- Compiled code
Columnar storage
Columnar storage for database tables is an important factor in optimizing analytic query performance because it drastically reduces the overall disk I/O requirements and reduces the amount of data you need to load from disk.
In a typical relational database table, each row contains field values for a single record. In row-wise database storage, data blocks store values sequentially for each consecutive column making up the entire row. If block size is smaller than the size of a record, storage for an entire record may take more than one block. If block size is larger than the size of a record, storage for an entire record may take less than one block, resulting in an inefficient use of disk space. In online transaction processing (OLTP) applications, most transactions involve frequently reading and writing all of the values for entire records, typically one record or a small number of records at a time. As a result, row-wise storage is optimal for OLTP databases.
Using columnar storage, each data block stores values of a single column for multiple rows. As records enter the system, Amazon Redshift transparently converts the data to columnar storage for each of the columns.
Workload management
Amazon Redshift workload management (WLM) enables users to flexibly manage priorities within workloads so that short, fast-running queries won’t get stuck in queues behind long-running queries.
Amazon Redshift WLM creates query queues at runtime according to service classes, which define the configuration parameters for various types of queues, including internal system queues and user-accessible queues. From a user perspective, a user-accessible service class and a queue are functionally equivalent. For consistency, this documentation uses the term queue to mean a user-accessible service class as well as a runtime queue.
When you run a query, WLM assigns the query to a queue according to the user’s user group or by matching a query group that is listed in the queue configuration with a query group label that the user sets at runtime.
Using Amazon Redshift with other services
Amazon Redshift integrates with other AWS services to enable you to move, transform, and load your data quickly and reliably, using data security features.
- Moving data between Amazon Redshift and Amazon S3
- Using Amazon Redshift with Amazon DynamoDB
- Importing data from remote hosts over SSH
- Automating data loads using AWS Data Pipeline
- Migrating data using AWS Database Migration Service (AWS DMS)
Thank you
Praveen Borra
YouTube Channel:
https://www.youtube.com/c/PraveenBorra

Leave a comment